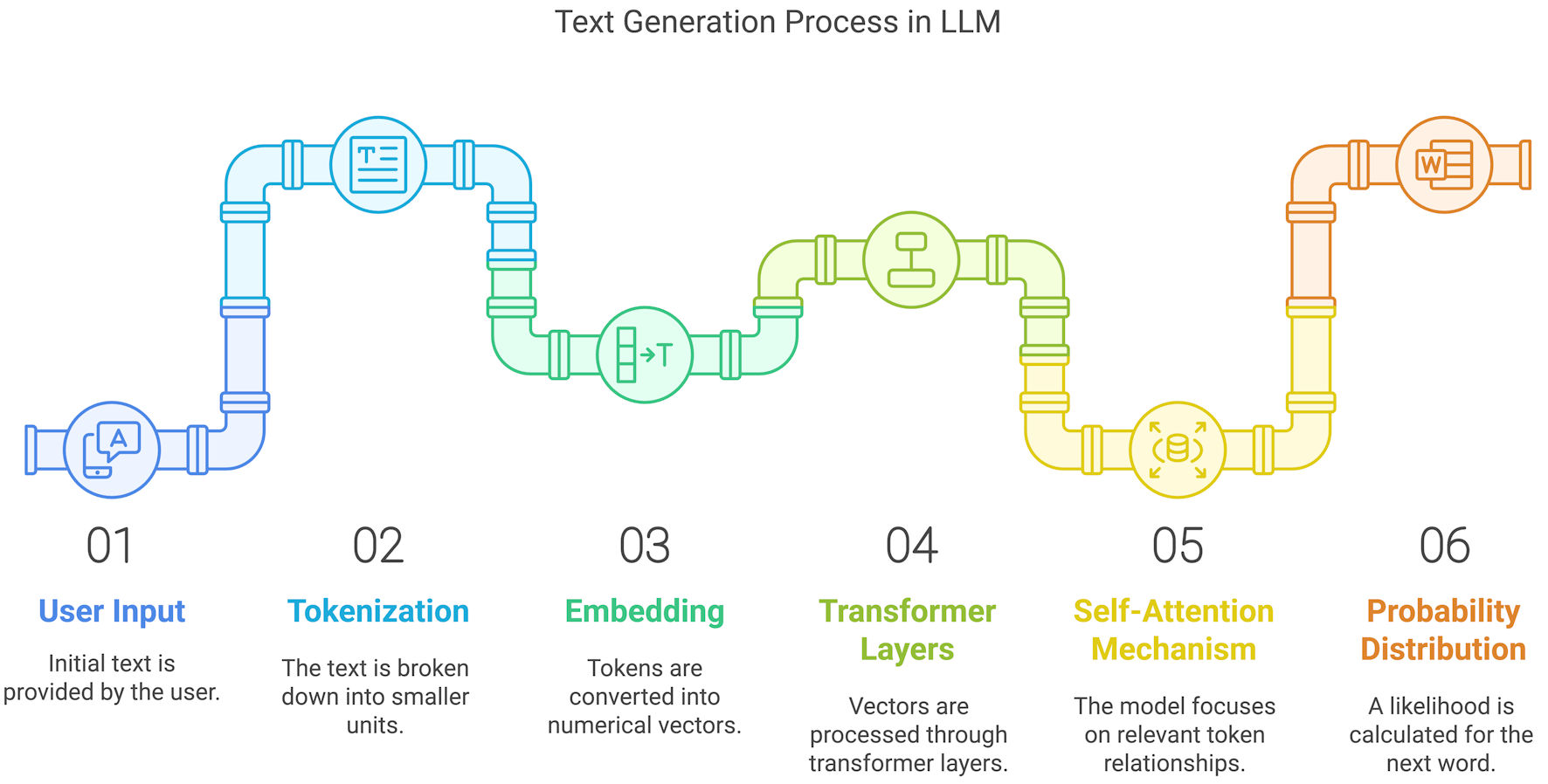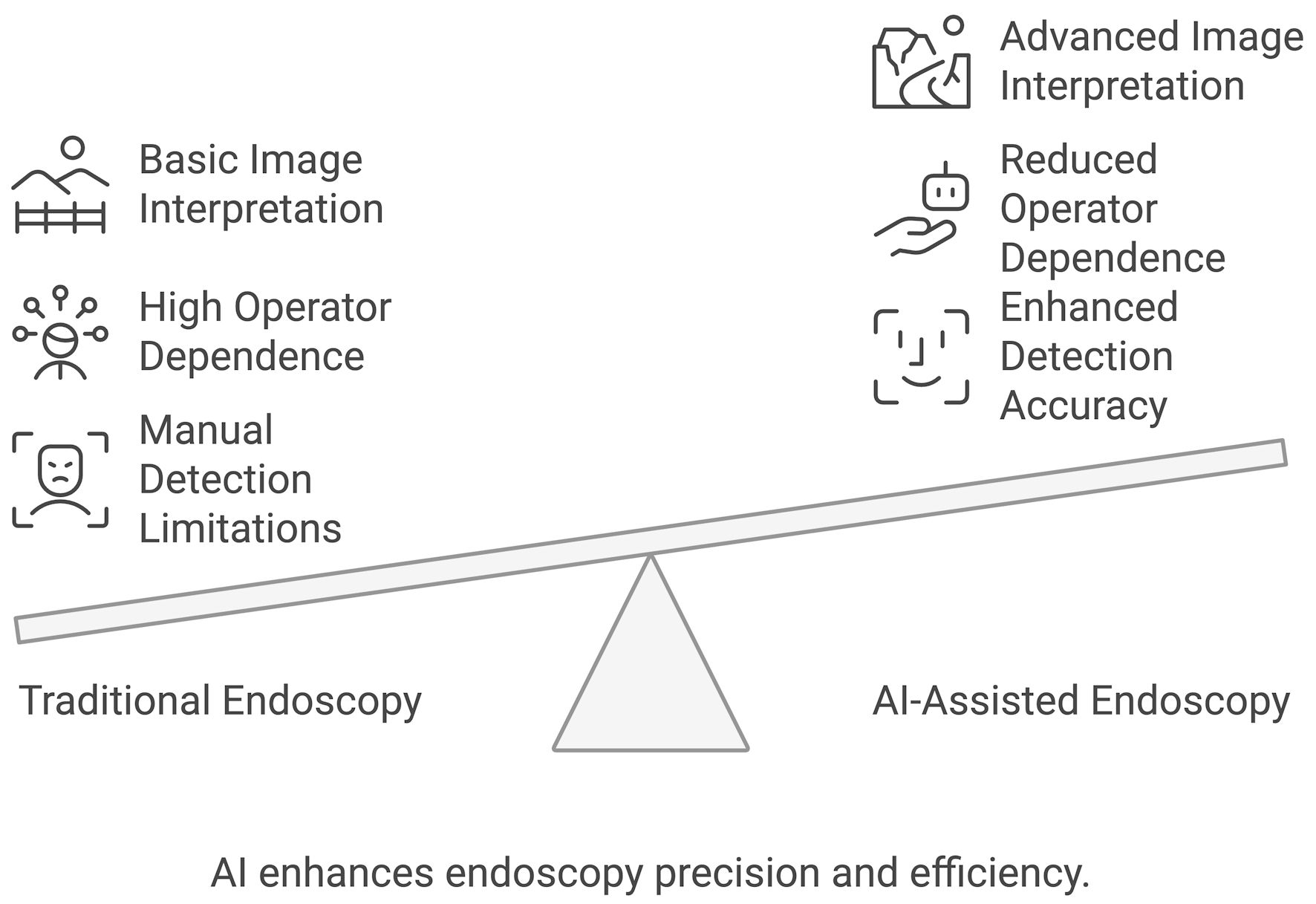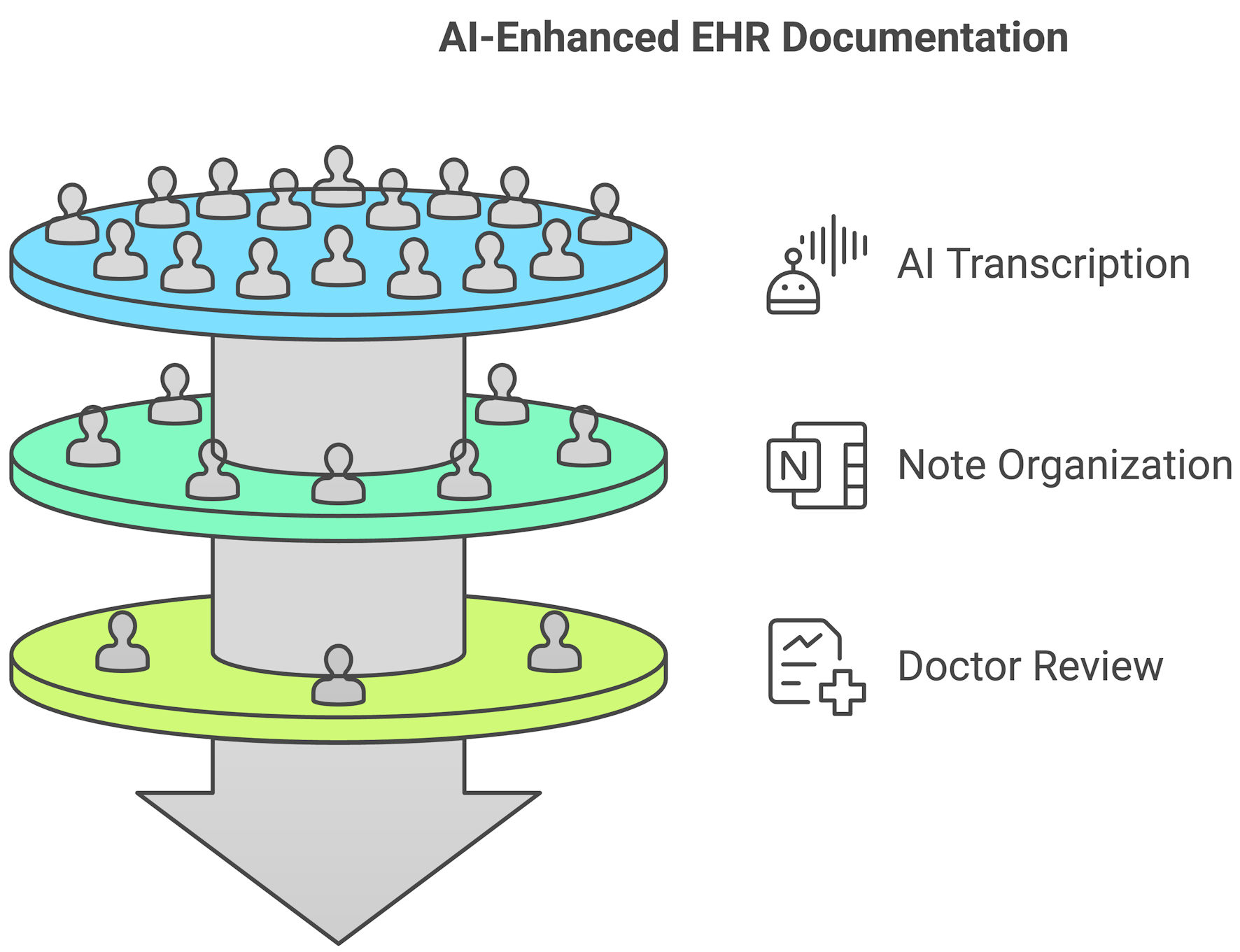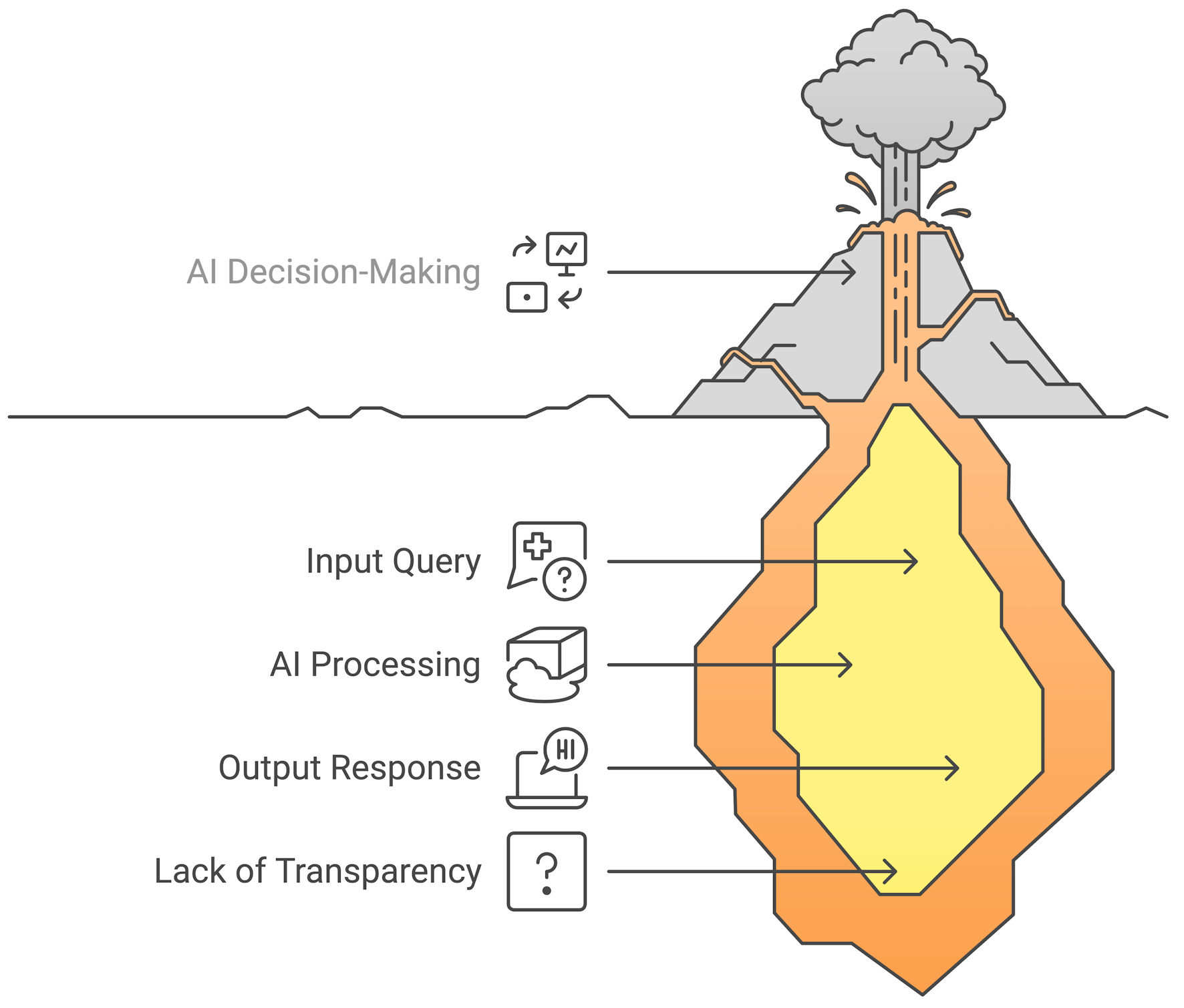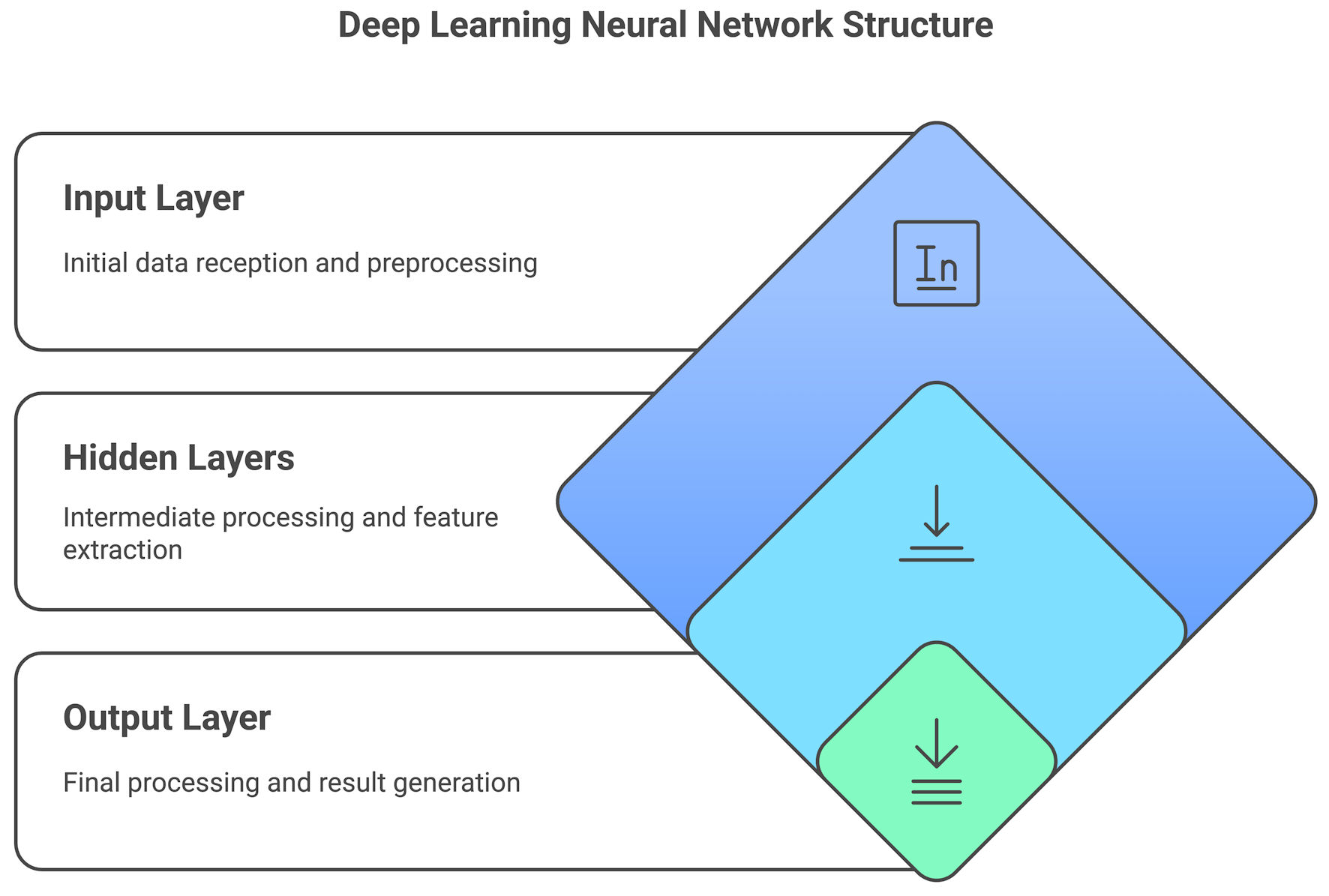
Figure 1. A deep learning neural network structure used in large language models (LLMs), including input, hidden, and output layers.
| Gastroenterology Research, ISSN 1918-2805 print, 1918-2813 online, Open Access |
| Article copyright, the authors; Journal compilation copyright, Gastroenterol Res and Elmer Press Inc |
| Journal website https://gr.elmerpub.com |
Review
Volume 18, Number 2, April 2025, pages 39-48
Large Language Models in Gastroenterology and Gastrointestinal Surgery: A New Frontier in Patient Communication and Education
Figures