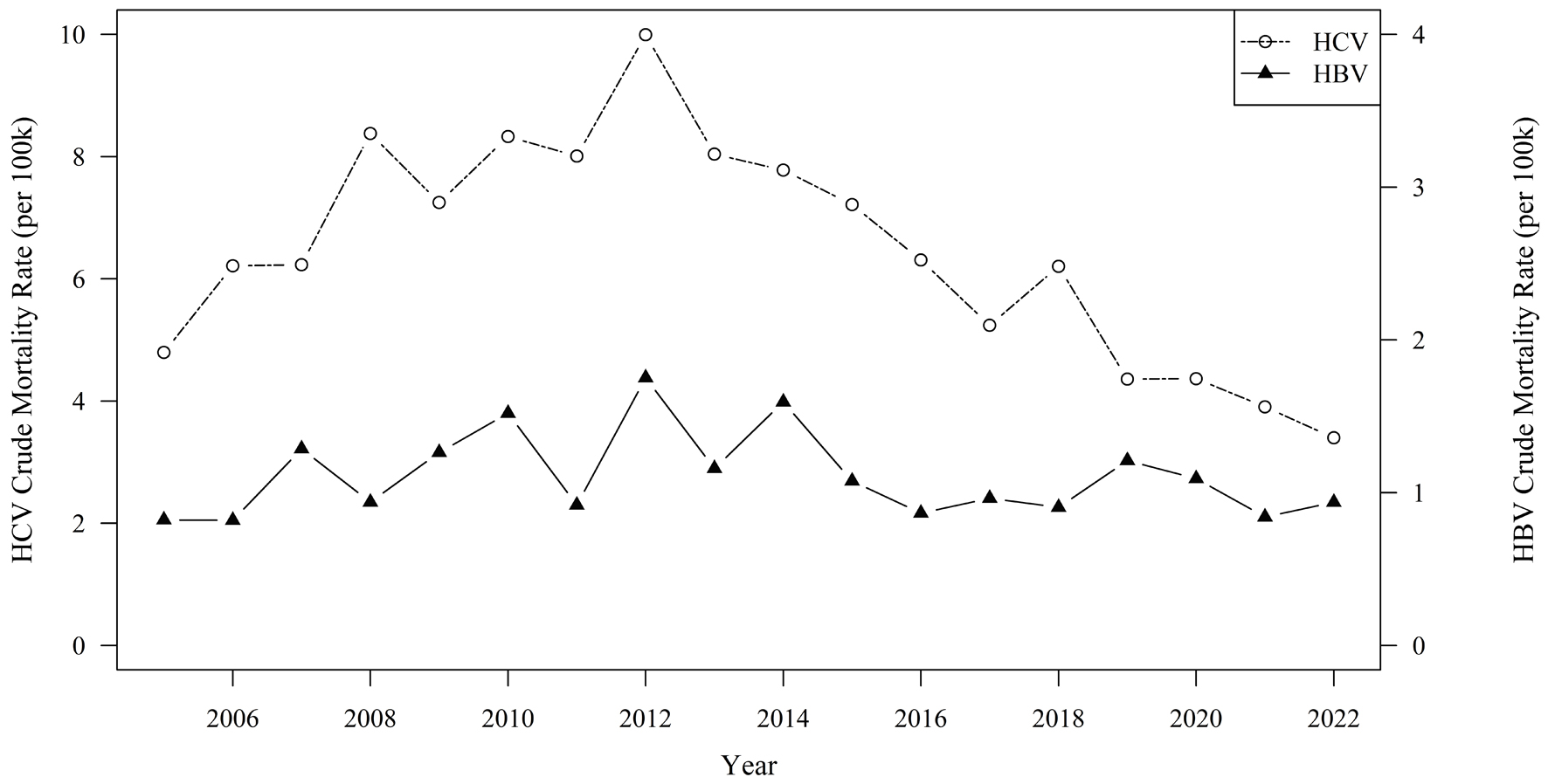
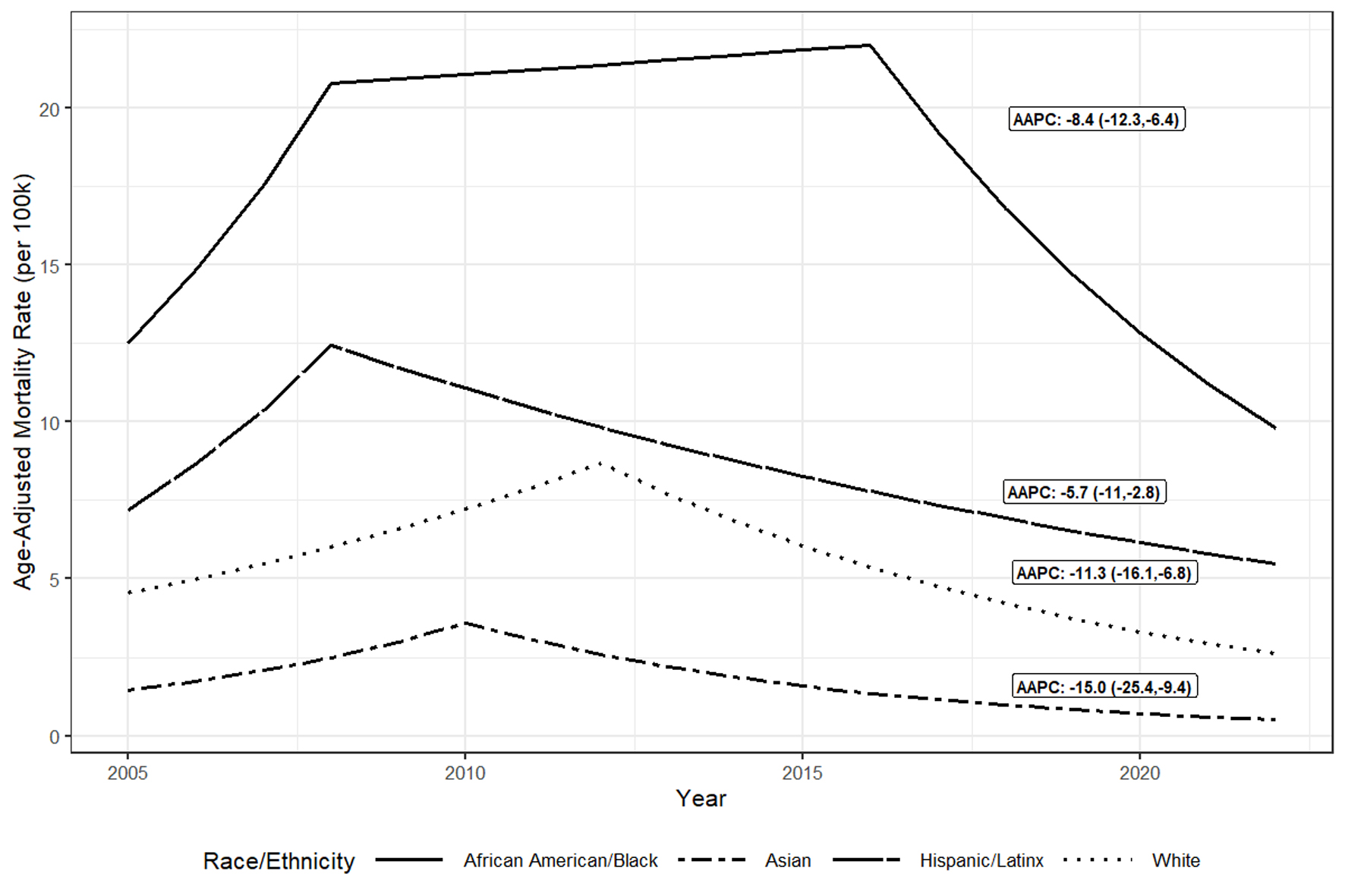
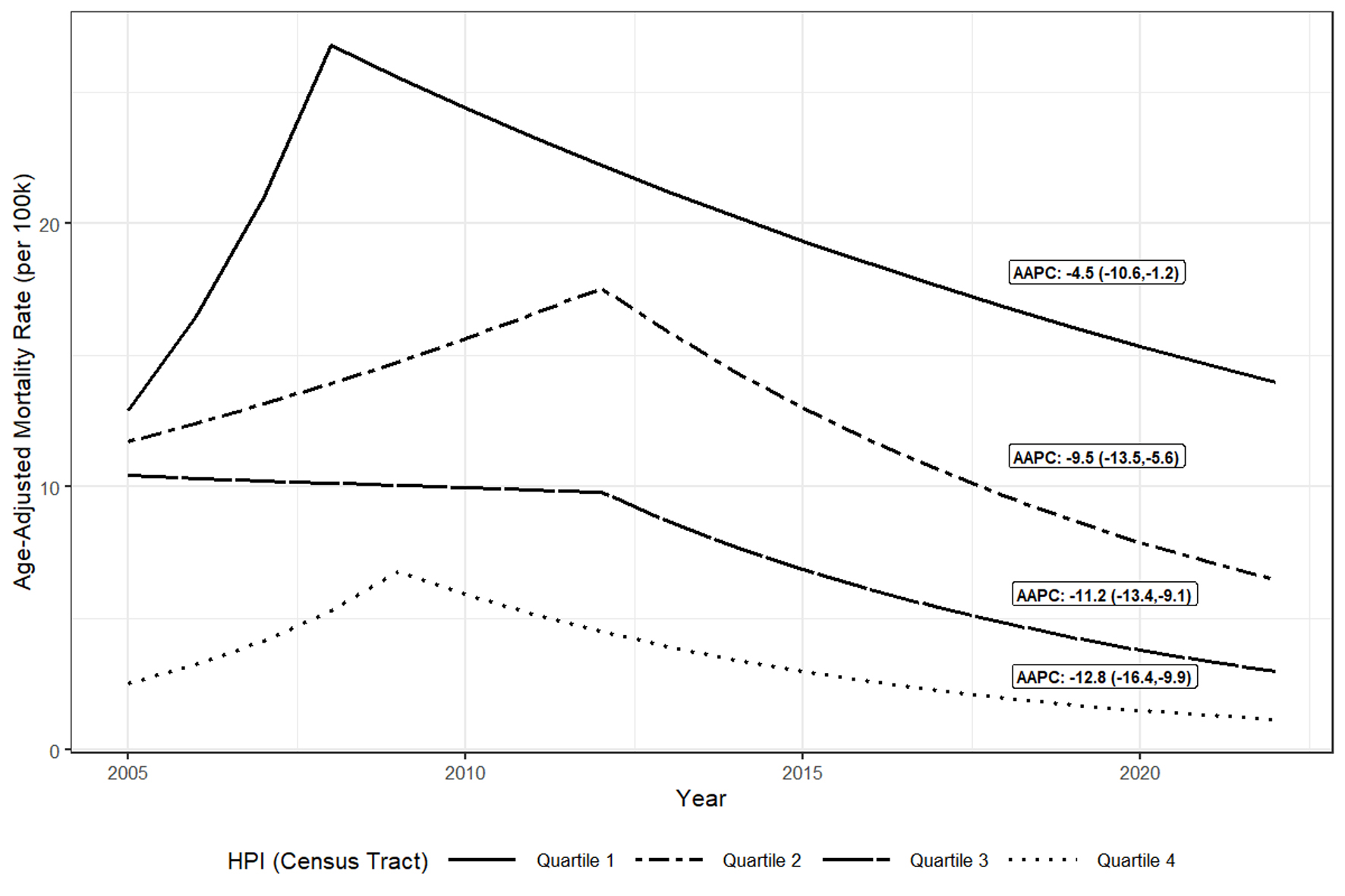
| aICD-10 coding definitions: HBV, B16, B17.0, B18.0, B18.1; HCV, B17.1, B18.2; HIV, B20.x-B24.x; diabetes, E10.x-E14.x; cardiovascular, IXX.x; drug dependence, X40.x-X44.x, Y10.x-Y16.x, X60.x-X64.x, F11.x, F13.x, F15.x; alcohol-associated liver disease, K70.x; hepatocellular carcinoma, C22.x, D37.6; cirrhosis, K71.7, K70.3, K74.1-K74.6; liver failure, K70.4, K72. bP value for tests of significance between HBV and HCV statuses. P value calculated using Kruskal-Wallis test for age and Chi-square test for all other variables. Note: Cells with counts < 10 and that are not unknown are suppressed as well as their complementary cells, indicated with a “-” to avoid inadvertent disclosure of identity. HBV: hepatitis B virus; HCV: hepatitis C virus; HIV: human immunodeficiency virus; HPI: Healthy Places Index; IQR: interquartile range. |