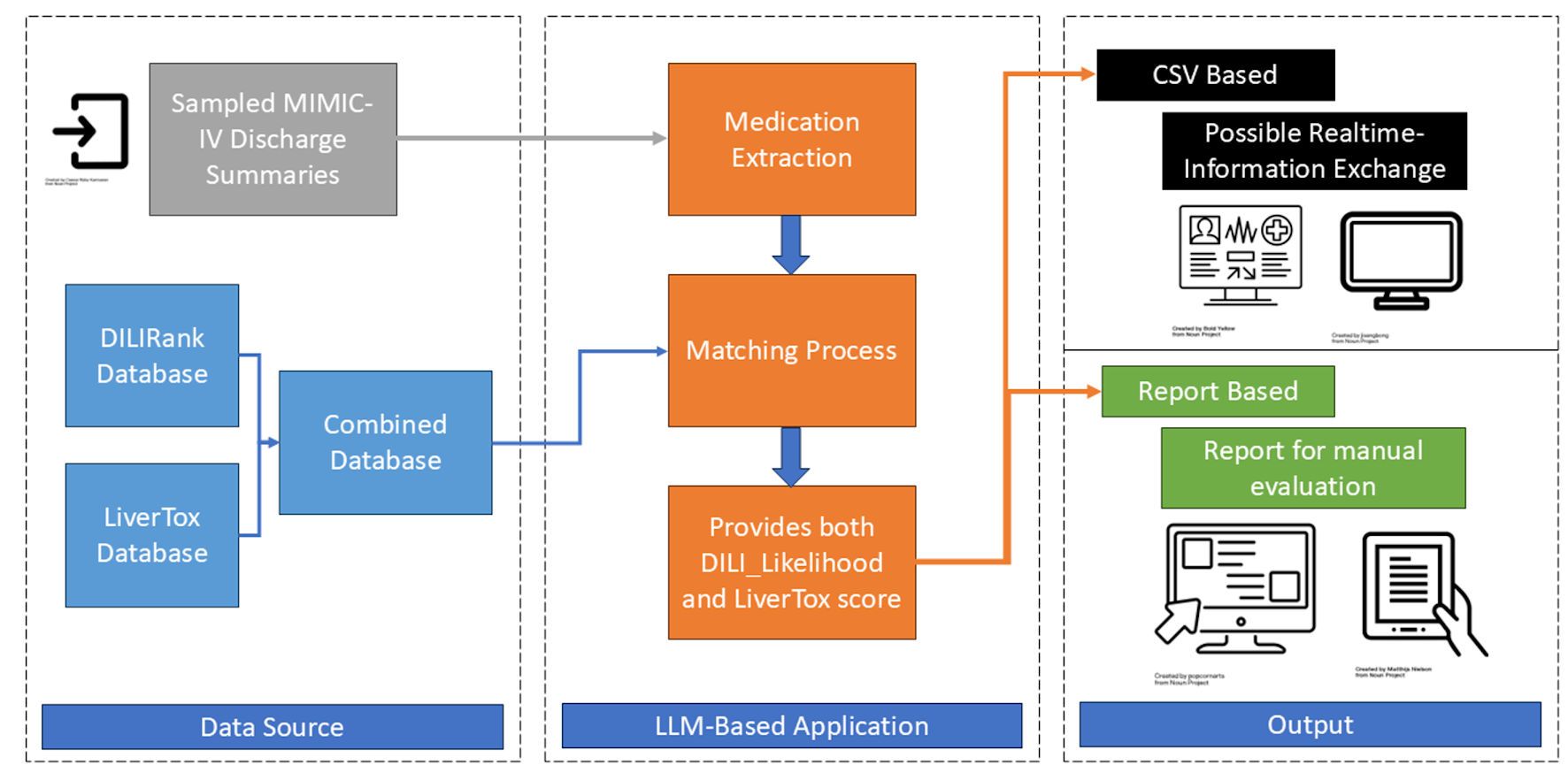
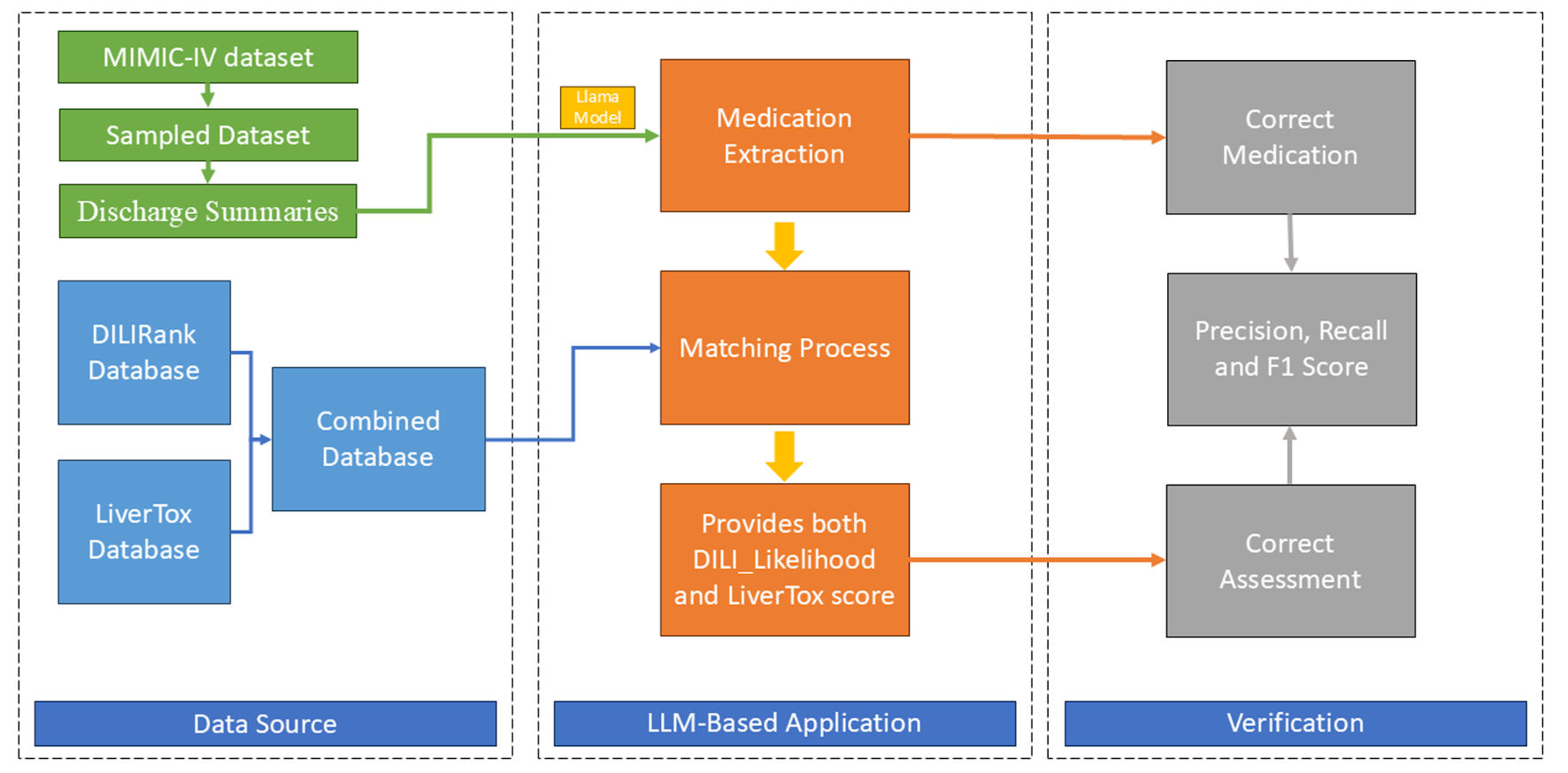
Figure 1. System architect. MIMIC-IV: Medical Information Mart for Intensive Care IV; DILI: drug-induced liver injury; LLM: large language models.
| Gastroenterology Research, ISSN 1918-2805 print, 1918-2813 online, Open Access |
| Article copyright, the authors; Journal compilation copyright, Gastroenterol Res and Elmer Press Inc |
| Journal website https://gr.elmerpub.com |
Original Article
Volume 18, Number 5, October 2025, pages 247-253
Enabling Drug-Induced Liver Injury Surveillance Through Automated Medication Extraction From Clinical Notes: A Medical Information Mart for Intensive Care IV Real-World Large Language Models Validation Study
Figures

Tables
| Data source | Description | Type | Sample size used | Total medications in sample | Source type |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MIMIC-IV: Medical Information Mart for Intensive Care IV; DILI: drug-induced liver injury; N/A: not applicable. | |||||
| MIMIC-IV | Sampled discharge summaries of MIMIC-IV | Unstructured data | 100 | 1,236 | Deidentified data |
| Combined DILI database | Merged DILIrank/LiverTox data | Reference database | N/A | About 1,200 unique entries (estimated) | Reference databases |
| MIMIC-IV dataset | |
|---|---|
| MIMIC-IV: Medical Information Mart for Intensive Care IV. | |
| Total discharge summary | 100 |
| Total medications | 1,236 |
| True positive | 996 |
| False positive | 174 |
| False negative | 0 |
| Precision | 0.85 |
| Recall | 1.00 |
| F1-score | 0.92 |