Statins and the Risk of Colorectal Cancer in Patients With Inflammatory Bowel Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.14740/gr2028Keywords:
Statins, Colorectal cancer, Inflammatory bowel disease, Odds ratio, Hazard ratioAbstract
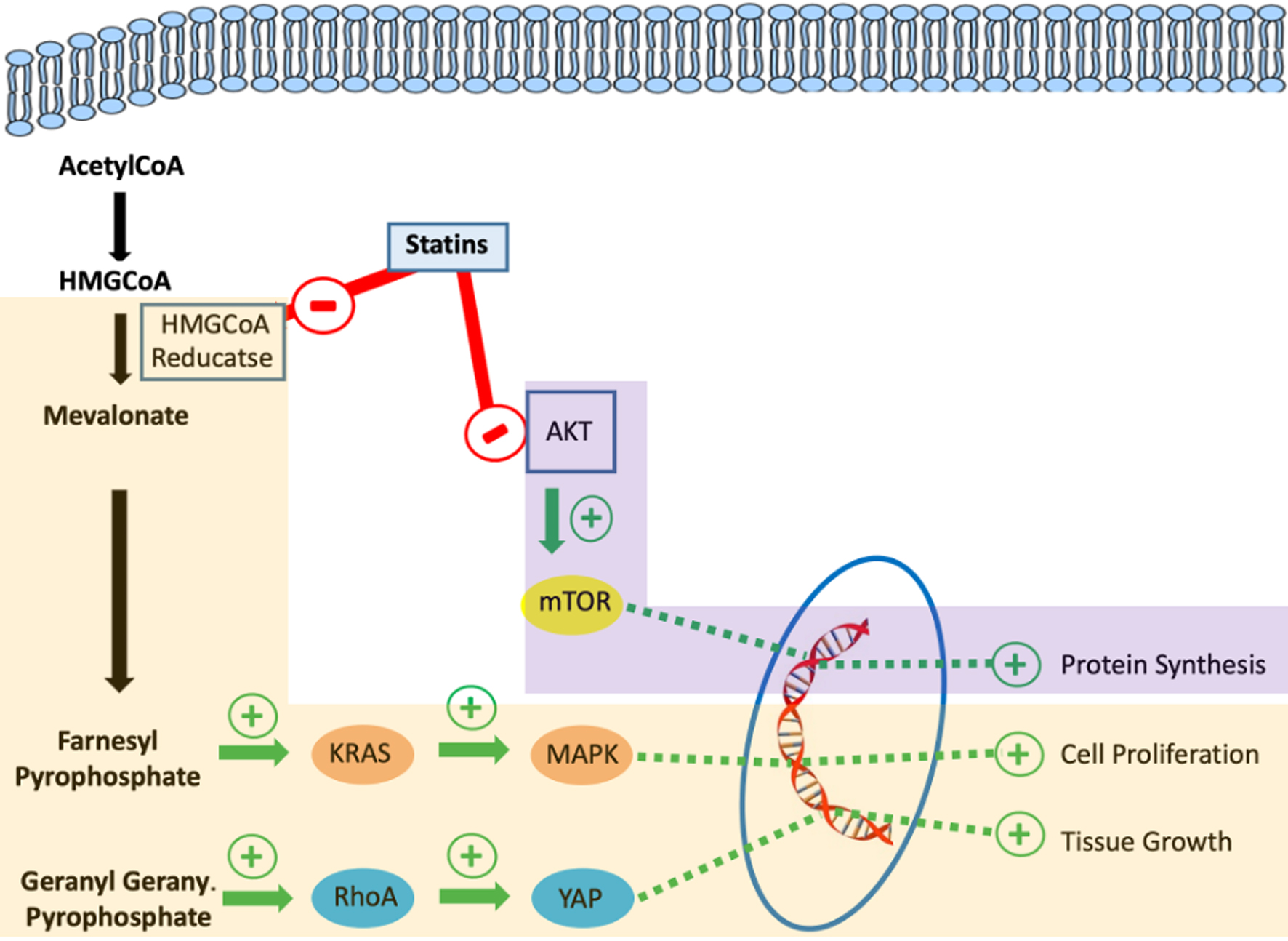
Background: Statins are reported to reduce colorectal cancer (CRC) risk in the general population, but their effect on individuals with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) remains uncertain. We aimed to evaluate the relationship between statin use and CRC risk in patients with IBD.
Methods: A comprehensive review of the literature was conducted on PubMed, Web of Science, and EMBASE to evaluate the association between statin use and the development of CRC in patients with IBD. After deduplication, there were 324 studies screened, and those reporting odds ratios (ORs) or hazard ratios (HRs) for CRC risk in IBD patients using statins were included. The primary endpoints included the development of CRC (OR) and time to CRC (HR). A meta-analysis utilizing fixed or random-effects models, heterogeneity tests, and a funnel plot was performed in R (version 4.3.0) with alpha of 0.05.
Results: This meta-analysis included seven studies involving 59,596 patients: three for OR (11,116 patients) and four for HR (48,480 patients). The pooled OR was 0.22 (95% confidence interval (CI): 0.01 - 7.81), suggesting 78% lower odds of CRC in statin users, though not statistically significant (P = 0.21), with potential publication bias. The pooled HR was 0.77 (95% CI: 0.63 - 0.94), indicating a significant 23% reduction in CRC hazard for statin users (P < 0.05), with low publication bias.
Conclusion: Our meta-analysis showed that statin use is associated with a reduced risk of CRC in IBD, significant in HR-based but not in OR-based analysis. Large randomized controlled trials are needed to clarify the duration of statin use and their chemopreventive effects, independent of factors such as targeted therapy for chronic mucosal inflammation.
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 The authors

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.









