Efficacy and Safety of Mycophenolate Mofetil Compared to Azathioprine in Autoimmune Hepatitis: A Meta-Analysis
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.14740/gr2044Keywords:
AIH, MMF, AZA, Treatment-naive, Intolerant, Non-responsive, Biochemical remission, Adverse eventsAbstract
Background: Mycophenolate mofetil (MMF) has been suggested as a potential alternative treatment option for patients who are intolerant or unresponsive to the standard corticosteroid and azathioprine (AZA) regimen for autoimmune hepatitis (AIH). This systematic review and meta-analysis aimed to comprehensively evaluate and compare the biochemical efficacy and safety profiles of MMF and AZA in the treatment of AIH.
Methods: This review systematically examined the available literature from the inception of the MEDLINE and EMBASE databases up to November 2024. The primary outcomes of interest included the evaluation of biochemical remission (BR), the effectiveness of MMF in patients who were non-responsive (AZA-NR) or intolerant to azathioprine (AZA-IT), and the assessment of adverse events (AEs) and overall survival.
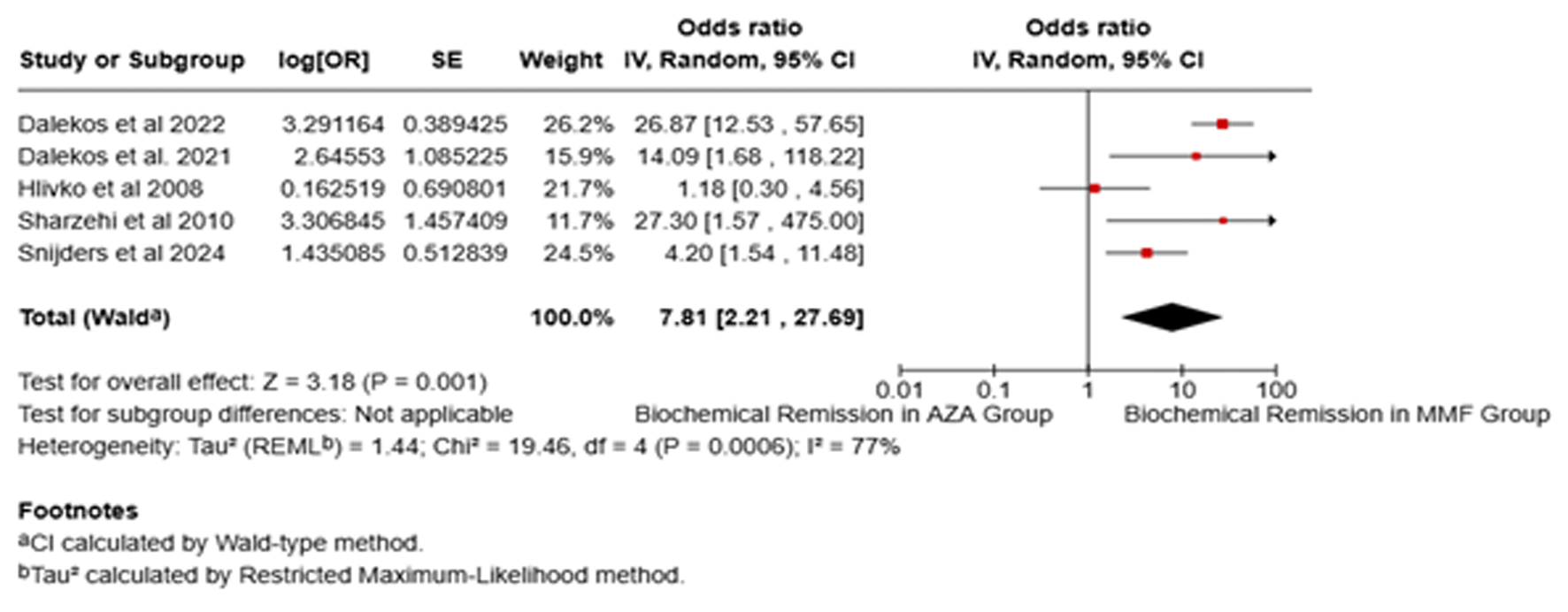
Results: This meta-analysis evaluated 11 studies comprising 952 participants, with 57.45% receiving MMF and the remaining receiving AZA. The findings indicate that MMF demonstrated a significantly higher BR rate (88.57%) than AZA (53.64%). The pooled analysis revealed a substantial improvement in the BR rate with MMF compared to AZA (odds ratio (OR): 7.81, 95% confidence interval (CI): 2.21 - 27.69). Furthermore, the estimated enhancement in treatment efficacy with MMF was 61% (95% CI: 42.63 - 78.04) among AZA-NR patients and 61.73% (95% CI: 54.88 - 68.35) in AZA-IT patients. However, the analysis did not reveal any significant differences between the two groups in terms of AEs (OR: 0.57, P = 0.47) and overall survival (OR: 1.27, P = 0.64).
Conclusions: MMF may be a suitable first-line alternative to AZA for AIH, with higher rates of BR, especially in patients intolerant or non-responsive to standard therapy. However, the long-term efficacy and safety of MMF requires further investigation through rigorous randomized controlled trials.
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 The authors

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.









