Acyl-CoA Synthetase Long-Chain Family Member 4 in Liver Injury: Multidimensional Regulation and Therapeutic Potential
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.14740/gr2098Keywords:
Acyl-CoA synthetase long-chain family member 4, Liver injury, Ferroptosis, Lipid peroxidation, Therapeutic potentialAbstract
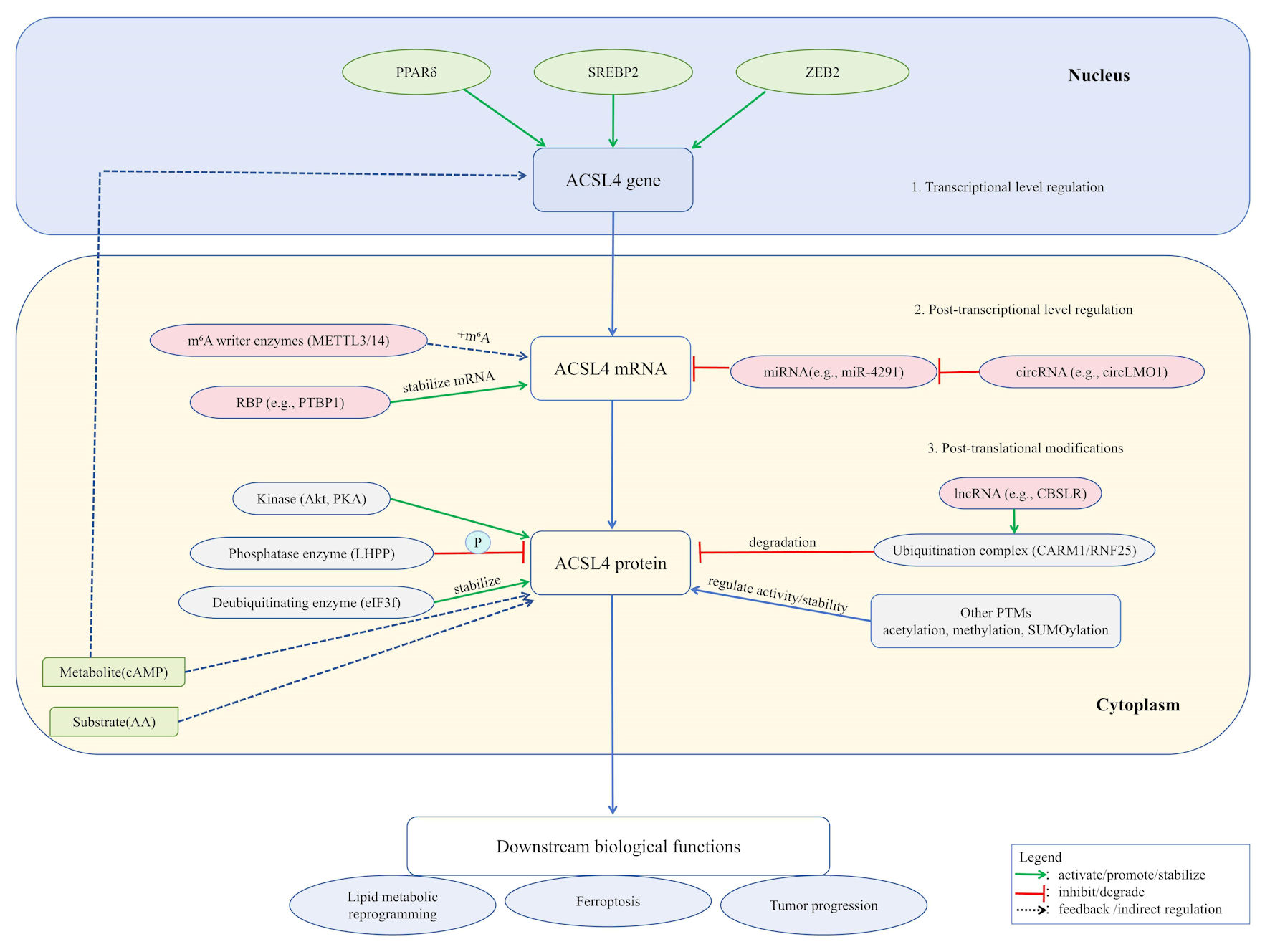
Acyl-CoA synthetase long-chain family member 4 (ACSL4) is a key enzyme that catalyzes the conjugation of long-chain fatty acids with coenzyme A to form acyl-CoA, showing particularly high specificity for polyunsaturated fatty acids. In recent years, ACSL4 has gained increasing attention for its central role in various liver diseases, including metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease, liver fibrosis, hepatocellular carcinoma, and ferroptosis. This article systematically elaborates on the expression profiles and localization of ACSL4 in different liver cell types, as well as its multidimensional regulatory mechanisms in liver injury and the pathogenesis of related diseases. In addition, it explores the potential therapeutic prospects of targeting ACSL4.
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2026 The authors

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.









